Miguel Uribe: What is a central nervous system hemorrhage, an episode that has him in critical condition?

In the last few hours , the Santa Fe de Bogotá Foundation issued a new health report on Senator Miguel Uribe Turbay, detailing his condition after suffering a central nervous system hemorrhage in the last 48 hours.
A central nervous system (CNS) hemorrhage refers to bleeding within the brain or its coverings (meninges), which represents a serious medical emergency.

Miguel Uribe Photo: MILTON DÍAZ. EL TIEMPO
It occurs when a blood vessel ruptures within the brain tissue, causing blood to accumulate in the parenchyma. It is a common form of hemorrhagic stroke, and its main causes include high blood pressure, arteriovenous malformations, aneurysms, tumors, and others.
2. Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) It occurs in the space between the brain and the arachnoid membrane (subarachnoid space). It is frequently caused by ruptured aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, or trauma, and is accompanied by symptoms such as severe headache, neck stiffness, and altered consciousness.
Management may include urgent CT, lumbar puncture, surgical clipping or embolization of the aneurysm, and ICU treatment.
3. Epidural hematoma Bleeding between the skull and the dura mater (the brain's protective outer layer). It usually results from trauma that ruptures blood vessels, especially the middle meningeal artery. It can cause a lucid interval followed by rapid neurological deterioration.
4. Subdural hematoma Accumulation of blood between the dura mater and the arachnoid. Caused by rupture of venous vessels due to trauma; common in older people or those on anticoagulation therapy. It is classified as acute (symptoms within the first 72 hours, with high mortality); subacute (3–21 days); and chronic (more than three weeks, slow accumulation, with a better prognosis).
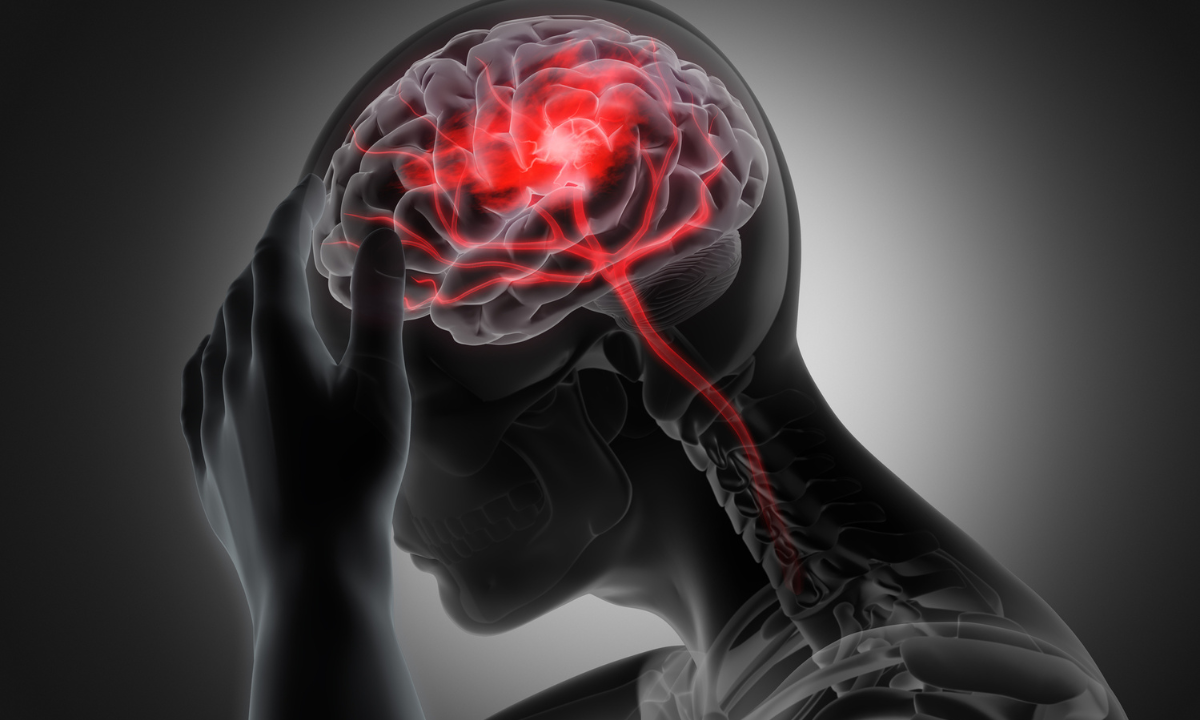
Main types of bleeding in the central nervous system Photo: istock
It occurs in the brainstem as a result of cerebral herniation (e.g., hippocampal uncus). It results from the rupture of perforating arteries.
eltiempo




