Scientists detect an unusual merger of dwarf galaxies in a cosmic void

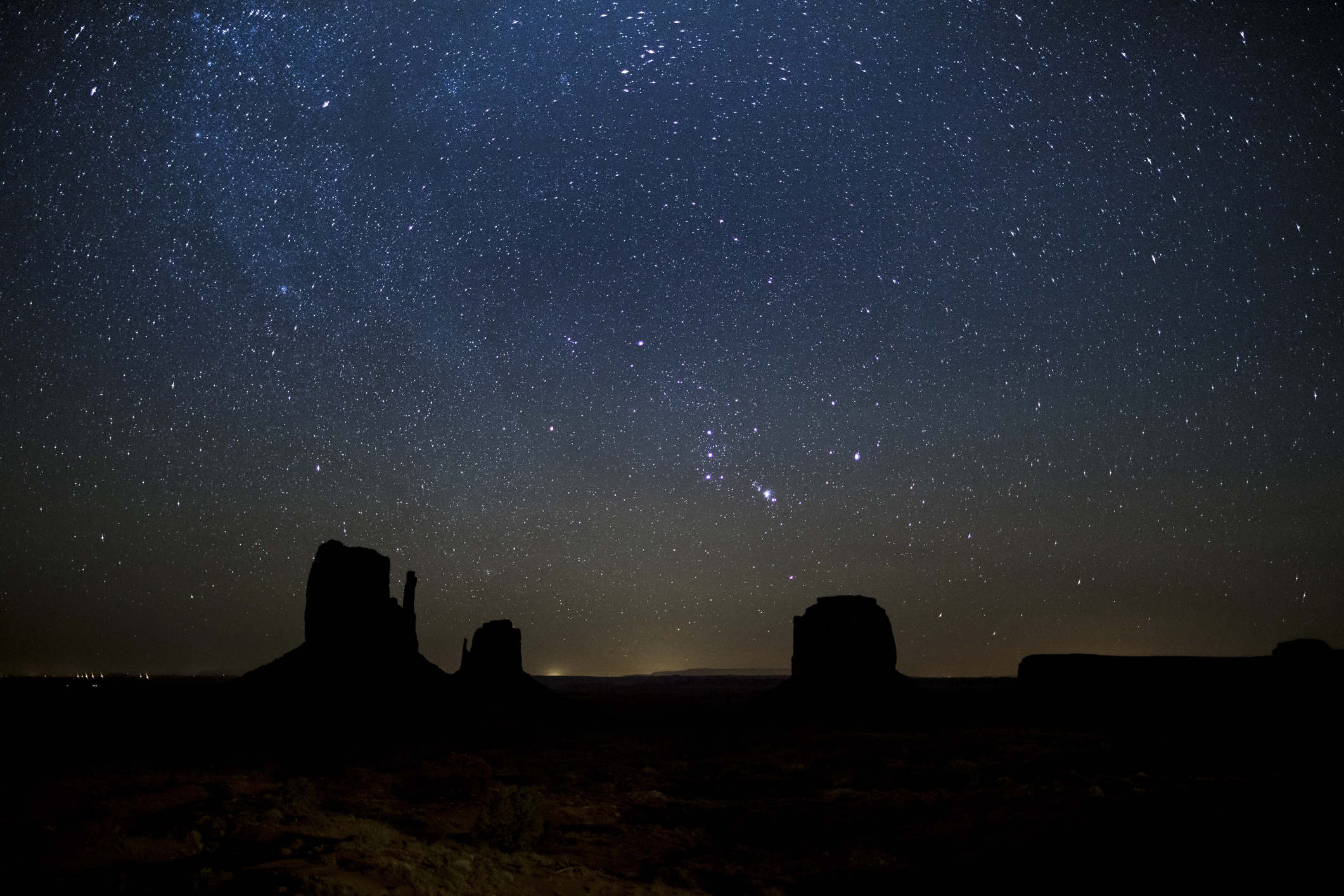
An international team of scientists, including the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), has observed in detail an ongoing merger between two low-mass dwarf galaxies located deep within a cosmic void , one of the least dense regions in the Universe.
The study is part of the Calar Alto Void Integral-field Treasury Survey (CAVITY) project, led by the University of Granada.
READ ALSO

The system, described as "extraordinary" by researchers, offers a unique opportunity to analyze how galaxies interact and evolve in extremely low-density environments, far from the cosmic web where these phenomena typically occur.
Unlike the common mergers between massive galaxies in dense regions, this case occurs in an isolated environment and between objects of similar masses.

This is what they revealed. Photo: iStock
Each galaxy involved has less than one-twentieth the mass of the Milky Way in terms of visible matter (stars, gas, and dust), and together they add up to about 10 billion solar masses.
The system features rotating gaseous disks and intense emission of ionized gas, indicative of a fusion-induced burst of star formation.
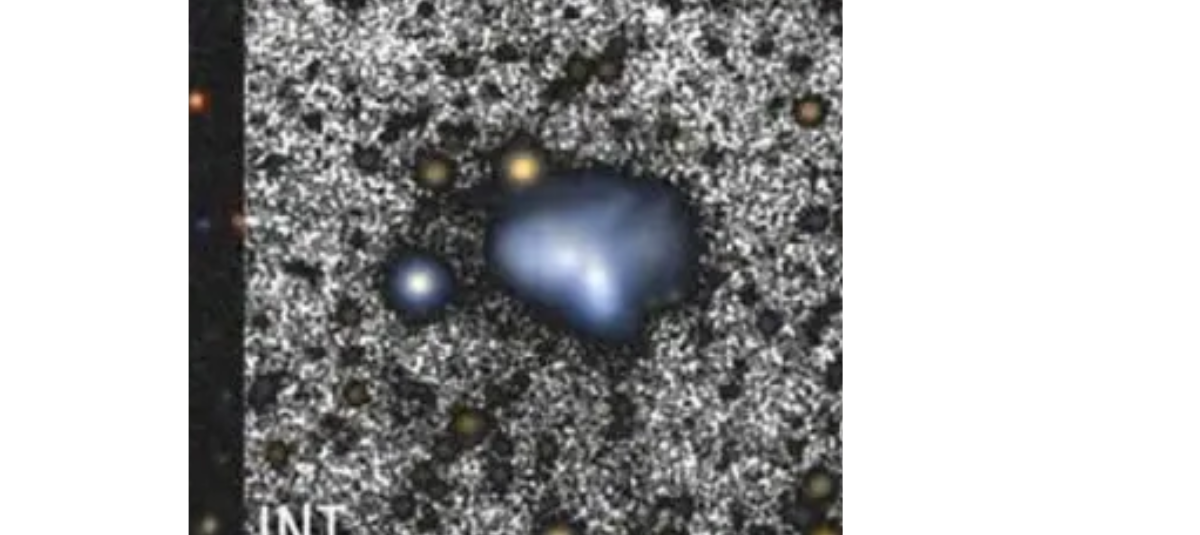
Rotating gaseous disks, ionized gas emission, and arcuate dust structures were detected. Photo: EFE
Thanks to a favorable alignment, the scientific team was able to measure the dynamic mass of each progenitor galaxy. Deep optical images taken with the Isaac Newton Telescope (INT), located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory (La Palma), also revealed arcuate dust structures possibly formed by shock fronts.

It occurs between two dwarf galaxies located in a cosmic void, one of the most sparsely populated regions. Photo: EFE
According to Bahar Bidaran, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Granada and lead author of the study, this merger does not follow typical patterns, such as collisions in galaxy clusters or between galaxies of different sizes. It is speculated that a prior interaction with a third dwarf galaxy or the dynamics of the cosmic void itself could have facilitated the encounter.
Importance of the discovery for cosmology The discovery provides valuable data on galactic evolution under extreme conditions. “This merger is a striking reminder that, even in the most isolated regions of the cosmos, galaxies can undergo dramatic transformations,” said Jesús Falcón-Barroso, IAC researcher and co-author of the study.
More news in EL TIEMPO *This content was rewritten with the assistance of artificial intelligence, based on information from EFE, and reviewed by the journalist and an editor.
eltiempo





