Man tells how a tooth infection nearly cost him his life: 'My tooth got infected, it caused a brain infection, and it was strange because I wasn't in pain.'

Graham Bell , a 61-year-old family man living in the UK, was preparing to leave on a trip with his wife Sue in March of this year when he began to experience a severe headache.
The situation became alarming when Sue noticed that his face seemed to have drooped to one side, a symptom commonly associated with a stroke . Upon seeing this, they both immediately went to a medical center for emergency care.
After being admitted, Graham was rushed to the Walton Centre NHS Foundation Trust in Liverpool. There, doctors detected a mass approximately one inch in size on his brain. This mass turned out to be an abscess, a collection of pus that results from an infection and can create pressure inside the skull, damaging brain cells and reducing blood flow , which can lead to brain tissue death.
The medical team identified the source of the problem: a crack in one of Graham's teeth that had caused an infection that spread without any obvious symptoms. "It was strange because I had no pain or swelling in my mouth to tell me anything was wrong," Graham said.
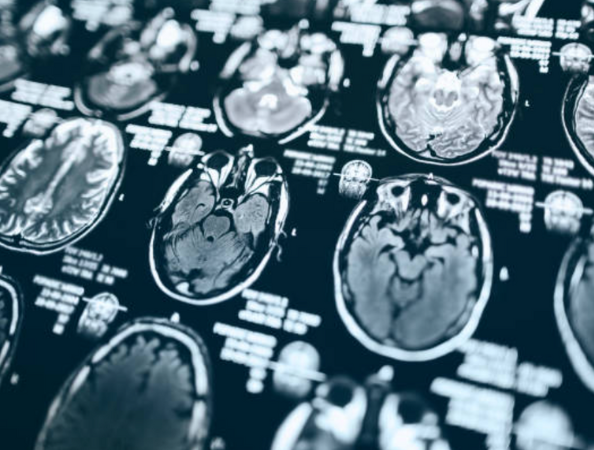
A headache revealed a brain infection caused by a damaged tooth. Photo: iStock
Surgery was immediate. The doctors performed "life-saving brain surgery," draining the abscess to relieve pressure on the brain.
Although the operation was successful and her condition began to gradually improve, days later, her symptoms returned. Doctors then determined that Graham was suffering from sepsis , an extreme immune system reaction to an infection that can cause the body to attack its own vital organs.
This new complication required a second surgery to drain the brain abscess again. The patient remained in recovery for six weeks. Although he made it through the critical phase, the damage left lasting effects. The scar tissue in the brain affected his communication and movement skills.
“He still has trouble communicating and moving, but we're continuing therapy and on the way to getting as close to normal as possible,” explained his wife, Sue.

Sepsis complicated Graham's recovery from a brain infection caused by a tooth. Photo: iStock
The medical explanation suggests that the bacteria present in dental infections can travel through the bloodstream and reach the brain through the sinuses. Once there, the infected tissue can accumulate in the form of pus, forming a brain abscess that, if not treated promptly, can have serious or even fatal consequences.
“It was a lot of information to absorb in a short amount of time. I had my family around me, but I think we were all a little shaken up. I wasn't well, so figuring out what was going on quickly was key for all of us,” Graham recalled.
What are the initial symptoms of a dental infection that can become complicated? An untreated dental infection can lead to a periapical abscess, a collection of pus caused by a bacterial infection that forms at the tip of the tooth root.
This type of abscess, according to the Mayo Clinic, is usually caused by untreated deep cavities, dental injuries, or previous treatments that have failed. Bacteria can enter the inside of the tooth through a cavity or crack, causing inflammation that can spread and cause serious complications if not treated promptly.
An untreated dental infection can lead to an abscess. Photo: iStock
Early symptoms of a dental abscess that may indicate a possible complication include:
- Constant, intense, stabbing toothache that may radiate to the jaw, neck, or ear.
- Sensitivity to heat and cold.
- Pain when chewing or biting.
- Fever.
- Swelling in the face, cheeks, or neck, which may make breathing or swallowing difficult.
- Swollen and tender lymph nodes under the jaw or in the neck.
- Bad smell or unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Sudden presence of foul-smelling salty fluid in the mouth, accompanied by pain relief, if the abscess ruptures.
Mayo Clinic recommends seeing a dentist immediately if you experience any of these symptoms. In more severe cases, such as fever accompanied by facial swelling, or difficulty breathing or swallowing, you should seek care in an emergency room.
El Universal (Mexico) / GDA
*This content was rewritten with the assistance of artificial intelligence, based on information from El Universal, and reviewed by a journalist and an editor.
eltiempo




